ThisAssembly.Vsix
2.0.9
Prefix Reserved
dotnet add package ThisAssembly.Vsix --version 2.0.9
NuGet\Install-Package ThisAssembly.Vsix -Version 2.0.9
<PackageReference Include="ThisAssembly.Vsix" Version="2.0.9"> <PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets> <IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers</IncludeAssets> </PackageReference>
paket add ThisAssembly.Vsix --version 2.0.9
#r "nuget: ThisAssembly.Vsix, 2.0.9"
// Install ThisAssembly.Vsix as a Cake Addin #addin nuget:?package=ThisAssembly.Vsix&version=2.0.9 // Install ThisAssembly.Vsix as a Cake Tool #tool nuget:?package=ThisAssembly.Vsix&version=2.0.9
This project uses SponsorLink to attribute sponsor status (direct, indirect or implicit). For IDE usage, sponsor status is required. IDE-only warnings will be issued after a grace period otherwise.
Allows consuming VSIX manifest properties from code, as well as MSBuild project properties from the VSIX manifest. For example:
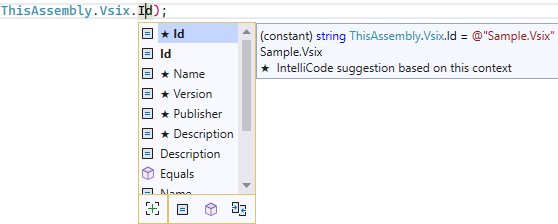
In addition to making the VSIX manifest metadata
properties available as constants, the package also provides targets for those properties
with sensible defaults from project properties so that the manifest can leverage
placeolder syntax
and avoid duplication in the source.extension.vsixmanifest:
<PackageManifest Version="2.0.0" ...>
<Metadata>
<Identity Id="|%CurrentProject%;VsixId|" Version="|%CurrentProject%;VsixVersion|" Language="|%CurrentProject%;VsixLanguage|" Publisher="|%CurrentProject%;VsixPublisher|" />
<DisplayName>|%CurrentProject%;VsixDisplayName|</DisplayName>
<Description>|%CurrentProject%;VsixDescription|</Description>
</Metadata>
...
</PackageManifest>
The available properties and their default values are:
| Name | Default Value |
|---|---|
| VsixID | $(PackageId) or $(AssemblyName) |
| VsixVersion | $(Version) |
| VsixDisplayName | $(Title) |
| VsixDescription | $(Description) |
| VsixProduct | $(Product) |
| VsixPublisher | $(Company) |
| VsixLanguage | $(NeutralLanguage) or 'en-US' |
As shown in the example above, the syntax for using these properties from the source.extension.vsixmanifest is
|%CurrentProject%;[PROPERTY]|. This is because the package defines a corresponding target to
retrieve each of the above properties. You can provide a different value for each property via
MSBuild as usual, of course.
Since the $(PackageId) property can be used as the VSIX ID, the Pack target is redefined to
mean CreateVsixManifest, so "packing" the VSIX is just a matter of right-clicking the VSIX
project and selecting "Pack".
Customizing the generated code
Set the $(ThisAssemblyNamespace) MSBuild property to set the namespace of the
generated ThisAssembly root class. Otherwise, it will be generated in the global namespace.
The generated root ThisAssembly class is partial and has no visibility modifier by default,
making it internal by default in C#.
You can set the $(ThisAssemblyVisibility) MSBuild property to public to make it public.
This will also change all constants to be static readonly properties instead.
Default:
partial class ThisAssembly
{
public partial class Constants
{
public const string Hello = "World";
}
}
In this case, the compiler will inline the constants directly into the consuming code at the call site, which is optimal for performance for the common usage of constants.
Public:
public partial class ThisAssembly
{
public partial class Constants
{
public static string Hello => "World";
}
}
This makes it possible for consuming code to remain unchanged and not require
a recompile when the the values of ThisAssembly are changed in a referenced assembly.
If you want to keep the properties as constants, you can instead extend the generated code by defining another partial that can modify its visibility as needed (or add new members).
// makes the generated class public
public partial ThisAssembly
{
// Nested classes are always public since the outer class
// already limits their visibility
partial class Constants
{
// add some custom constants
public const string MyConstant = "This isn't configurable via MSBuild";
// generated code will remain as constants
}
}
Sponsors
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net5.0 was computed. net5.0-windows was computed. net6.0 was computed. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 was computed. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 was computed. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. |
| .NET Core | netcoreapp2.0 was computed. netcoreapp2.1 was computed. netcoreapp2.2 was computed. netcoreapp3.0 was computed. netcoreapp3.1 was computed. |
| .NET Standard | netstandard2.0 is compatible. netstandard2.1 was computed. |
| .NET Framework | net461 was computed. net462 was computed. net463 was computed. net47 was computed. net471 was computed. net472 was computed. net48 was computed. net481 was computed. |
| MonoAndroid | monoandroid was computed. |
| MonoMac | monomac was computed. |
| MonoTouch | monotouch was computed. |
| Tizen | tizen40 was computed. tizen60 was computed. |
| Xamarin.iOS | xamarinios was computed. |
| Xamarin.Mac | xamarinmac was computed. |
| Xamarin.TVOS | xamarintvos was computed. |
| Xamarin.WatchOS | xamarinwatchos was computed. |
-
.NETStandard 2.0
- Microsoft.VSSDK.BuildTools (>= 17.0.5240)
- ThisAssembly.Constants (>= 2.0.9)
NuGet packages
This package is not used by any NuGet packages.
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
